The way businesses operate today is completely different from three years ago. From AI-driven processes to multi-cloud infrastructures and remote-first teams, modern companies run on various numbers of applications that must be able to “talk” to each other for a smoother workflow.
This shift isn’t small. The need for connected systems has grown so much that, according to Gartner, the integration software market reached US$ 34.8 billion and is growing at nearly 10.9% every year.
But here’s the real problem. The more tools companies add, the more disconnected their systems become. That’s exactly where software integration steps in, not as an option, but as the foundation of scalable, future-ready business operations.
This guide breaks down what software integration really means, how it works behind the scenes, the types you must, challenges developers face in integration and how to overcome them.
What Is Software Integration?
Imagine every software tool you use, CRM, ERP, analytics dashboards, HRMS, ticketing systems, marketing tools as workers inside a big corporation. Now imagine all of them work independently, never exchange information, never update each other, and never collaborate.
What do you think will be the result? Ofcourse. That business collapses in weeks. Software integration solves that exact problem by allowing all systems to:
- Share data
- Trigger actions
- Synchronize records
- Communicate automatically
- Reduce manual tasks
- Deliver a single source of truth
Software integration is the process of connecting multiple applications that otherwise work independently. This leads to smooth sharing of data, better actions, and functioning in a similar manner across platforms. So instead of working in isolation, all your apps such as CRM, ERP, HRMS, billing tools, and analytics become a big digital ecosystem.
What does integration give you?
- Automated data flow
- Real-time updates
- Better decision-making
- Zero manual data entry
- Unified dashboards
- Higher operational efficiency
- Reduced human errors
- Faster business outcomes
Instead of employees juggling spreadsheets, software integration creates a connected backbone where everything “just works.”
For Example: When you choose uber to book a cab, there are so many applications that are working within it, such as Uber itself, then you have Google maps, GPS, SMS options and payment options like UPI and cards.
While you just tap “book ride” all five of the applications are working at the backend and this is only possible with software integration.
Why Software Integration Matters More in 2026?
2026 isn’t “traditional IT” anymore. Businesses don’t use 5–6 tools, now they use 30 to 80+ depending on size. Various enterprise failures are due to poor system integration duplicate data, system misalignment and broken workflows.
This is why Integration is no longer something you add “later.” It is the infrastructure layer that decides how fast and efficiently your business will operate. Lets have a look at some leading factors making software integration important in the upcoming year and beyond.
AI Needs Clean Data
AI tools today work on all-time data streams. Unless your systems are integrated, your AI models process old, less consistent, or incomplete information – killing accuracy, slows down decisions, and restricts automation throughout the main business actions.
Multi-Cloud Requires Sync
The integration is the foundation with companies executing the workloads in AWS, Azure, GCP, and their own clouds. In the absence of integrative data flow, environments become chaotic, and expenses increase, as well as teams fail to keep an eye on the distributed systems.
Customer Journeys Break
Customers move between apps, channels, and touchpoints. Unless CRM, the marketing tools, support platforms, and billing are combined, the experience breaks down. Integration helps each team view the same story, which makes it fast and personalized.
Manual Ops Can’t Scale
The business expansion in the upcoming future cannot afford the use of spreadsheets and handoffs. The built-in systems do away with duplications, burdensome operations and allow teams to be involved in high priority, revenue generating tasks instead of hunting information that has been dispersed across the departments.
Compliance Demands Unity
Regulations, now be it in finance, healthcare, logistics or SaaS require no less than open data trails. Software Integration helps to ensure that all transactions, updates and any action is recorded in a uniform manner which minimizes the risks of audit as well as protect the company against a breach of compliance.
Types of Software Integration
Before exploring how integrations are implemented or which ones matter most, it’s important to understand the categories. These are not random terms — they define how your systems will behave, scale, and communicate.
Let’s break them down.
-
API Integration
APIs work like translators between two apps, helping them talk to each other without confusion. They pass information instantly, so tools like payment apps, CRMs, or delivery systems stay updated the moment something happens. It’s the technology that quietly keeps your daily apps in sync.
They share:
- Data
- Functionalities
- Real-time updates
Almost all modern integrations such as CRMs, payments, and marketing tools run on APIs.
Where it’s used: Payment gateways, CRMs, automation systems, logistics networks, AI workflows, e-commerce.
-
Data Integration
Data integration collects information from different tools and puts it in one clean place. Instead of teams checking ten dashboards, everything flows into one view you can trust. It helps leaders make decisions based on complete, accurate data — not guesswork.
This is all about merging data from multiple sources into:
- data warehouse
- BI dashboard
- unified analytics system
Useful when a company wants a single source of truth.
-
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)
This connects the important systems that run the everyday operations of a company. When HR, finance, CRM, and ERP are able to connect with each other smoothly, the entire business runs faster. It removes the gaps that usually slow teams down. This connects mission-critical systems like:
- ERP
- HRMS
- Finance
- CRM
- Manufacturing software
Think of it as the central nervous system for enterprise-level operations.
-
Cloud Integration
As companies store information across multiple cloud platforms, cloud integration keeps everything connected. No matter where the data lives, teams can access it as one unified system. Cloud integration helps in moving data in a smooth manner across:
- AWS
- Google Cloud
- Azure
- Private cloud tools
-
AI & Automation Integration
AI tools today are literally used everywhere. Gone are the days when humans use to do various tasks manually. AI tools are today in everyday workflow connecting with existing systems, making work easier and faster.
AI tools like:
- RPA bots
- Predictive engines
- AI-powered analytics
- Smart recommendation system
Software integration of these tools into existing workflows makes things easier. Your integration approach often depends on the frameworks your applications are built on. To understand which ones are leading the industry, see our list of the Top 10 Software Development Frameworks.
Software Integration vs System Integration
With both these terms sounding similar, many people often get confused, are they the same or not? Well to answer first, no they are not, and to make things clearer here is a clear differentiation of both.
| Factor | Software Integration | System Integration |
| Definition | Connecting two or more software applications to share data and workflows. | Combining hardware, software, networks, and infrastructure into a unified system. |
| Primary Focus | App-to-app communication and data exchange. | End-to-end ecosystem functionality across multiple components. |
| Scope | Narrow → focuses on specific tools or applications. | Broad → covers servers, devices, databases, networks, and software. |
| Complexity Level | Moderate, depending on APIs and data formats. | Higher, due to multiple moving parts and infrastructure layers. |
| Key Components | APIs, plugins, databases, and cloud apps. | Hardware, operating systems, networks, middleware, and security. |
| Main Goal | Streamline processes between apps. | Create a fully connected, seamless operational environment. |
| Time Required | Usually shorter (weeks). | Usually longer (months). |
| Common Challenges | Data mismatches, API limits, version conflicts. | Hardware compatibility, network issues, and scalability concerns. |
| Who Handles It | Software developers and API engineers. | System architects, IT infrastructure teams, network engineers. |
| Examples | CRM ↔ Email tool, ERP ↔ Accounting software. | POS system + servers + networking + database + custom software. |
How Software Integration Actually Works
If you are curious to know how this works, like how one thing can be the center of all the relevant apps around it. Have a look at this software integration process:
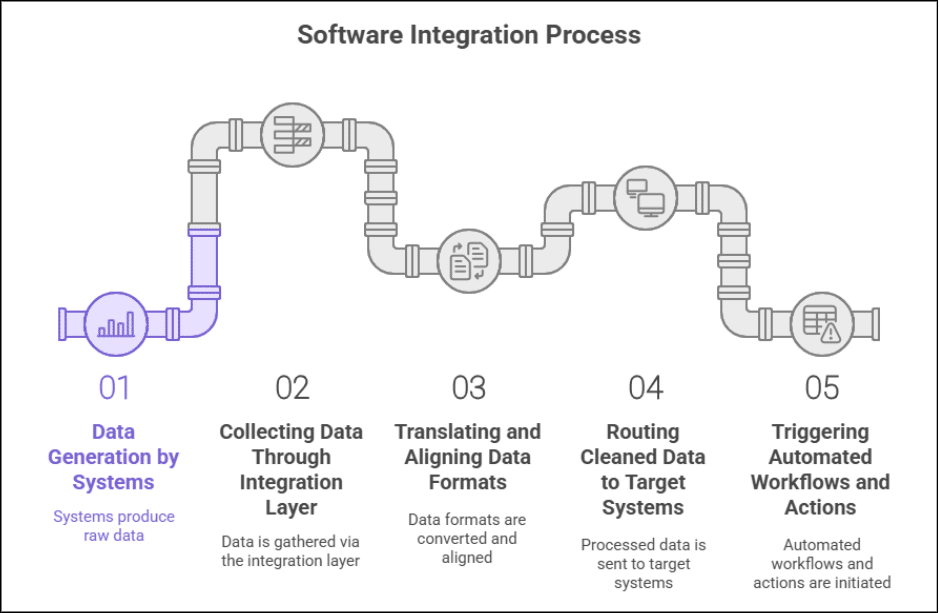
-
Your systems generate data
Every tool you use is constantly producing small pieces of information a customer signing up, an order placed, an invoice created, an employee checking in, and a support ticket being filed. All of this becomes raw data, scattered across different apps.
-
The integration layer collects that data
This is the “bridge” that pulls information from different systems. It can be through APIs, middleware platforms like Mulesoft or Zapier, or custom-built connectors. Think of it as a central pipeline that brings together everything your apps want to share.
-
The data gets translated and aligned
Here’s where the magic happens. Every system stores and formats information in its own way some call it “customer,” others say “client,” some use IDs, others use emails. Integration standardizes all of this, so every tool understands the data without confusion.
-
The cleaned data is sent to the right systems
Once the integration layer knows what the information means, it delivers it exactly where it needs to go. It might move order data from e-commerce to inventory, customer updates from CRM to ERP, or employee records from HR to payroll. Each system receives the right information at the right time.
-
Automation kicks in and triggers actions
This is the stage where you will actually see the real changes of software integration in your business.
A new lead enters → CRM updates → email tool adds them to a segment → AI scores the lead → Slack notifies sales
Everything happens in seconds, without anyone lifting a finger, manually entering data on sheets, writing various emails, etc . All because of software integration.
Where Does Different Types of Integrations Fits
Now many readers might have this question of with various types of software integration, how do I know when to use which.
Here is a at a glance table of the same. If you are still not sure how to use the right software integration, hire software developers who has the right knowledge and experience to integrate software using the right tech stack for a better and smoother business workflow.
| Integration Type | Best For | Examples | Why It Matters in 2026 |
| API Integration | SaaS tools, CRMs, automation | Stripe, Salesforce, HubSpot | Real-time data flow & faster automation |
| Data Integration | BI dashboards, warehouses | BigQuery, Redshift | Unified analytics & reporting accuracy |
| Cloud Integration | Multi-cloud workloads | AWS ↔ Azure | Reduces silos & boosts resource flexibility |
| Enterprise App Integration | ERP, HRMS, Finance | SAP, Oracle | Smooth enterprise workflows & zero duplication |
| AI & Automation Integration | Predictive workflows | RPA, GPT-based engines | Reduces manual work & boosts decision-making |
Seeing These Signs? Your Business Needs Integration Now!
While enterprises today do not really wait for the red flags to appear and integrate software prior to anything, yet if you have not done this and think things are going smoothly, make sure you don’t see the following signs. If so, it’s high time your business needed software integration.
- Your data is scattered across multiple tools
- Teams rely on spreadsheets to fill gaps
- Reports take hours or days to compile
- Customers complain about delays
- Two tools that should sync… don’t
- You’re entering the same data in multiple places
- Systems break whenever you scale
Know that every single one of these is costing time, money, and opportunities.
Software Integration Challenges and How to Overcome Them
As the business expands, it would naturally involve adding apps, more data sources, and automation and there are a reasonable portion of difficulties with it. These are the most ubiquitous ones that the team encounters nowadays, and what you can actually do to fix them.
The best way to escape these challenges is to get in touch with a professional software development company who knows how to tackle every challenge in software integration.
Too many disconnected systems
The vast majority of businesses up to now end up relying on various applications – CRMs, ERPs, HR tools, billing systems, analytics software, etc. These tools store information in their formats, and this makes it difficult to have a source of truth.
Fixing it: You begin by making a map of all of the systems you use, finding overlaps. Data format combined with middleware platforms (such as iPaaS services) is one of the ways you can align all of that without modifying your entire technology stack.
Inconsistent data across platforms
Platforms have inconsistencies in data. It is not so uncommon as people might believe that a customer is updated in one tool and not in another. These discrepancies do not merely cause confusion, they impact on reporting and judgment.
Fixing it: Determine explicit rules of data governance. Identify the most important system, which source holds each type of data, and then create automated synchronization policies based on that.
Excess reliance on engineering teams
There are still too many teams that overuse developers in carrying out small matters that entail integration. This paralyses the business process, and the other teams have to wait several weeks.
Fixing it: Low-code integration software and automation frameworks demarcate the procedure. Simple integrations can be created by your operations or marketing teams, which can help eliminate bottlenecks.
Scalability issues as the business grows
What works for a company with 1,000 records may fail miserably when you scale to a million.
Fixing it: Always choose tools that support horizontal scaling. Build integrations that can handle bigger data loads and spikes without manual tweaking.
Influence of AI and ML in Streamlining Software Integration
Earlier, developers had to manually map data, write connectors, test workflows, and keep fixing issues whenever one system changed. With growing data volumes and fast release cycles, this manual approach no longer scales. AI adds a layer of intelligence on top of traditional integration.
- it observes system patterns
- predicts failures
- automates repetitive tasks
- and keeps the entire integration flow healthier with minimal human intervention
It doesn’t replace developers, but it reduces the heavy lifting, so teams focus on the more complex decisions.
-
Smarter Data Mapping and Transformation
Data mapping is one of the slowest parts of integration. Every field needs to be matched, validated, and cleaned.
AI helps by:
- identifying patterns in data
- suggesting the best mapping automatically
- detecting inconsistencies early
- reducing the back-and-forth involved in manual mapping
This means faster onboarding of new data sources and fewer errors.
-
Automated Workflow Generation
Instead of manually designing integration flows step-by-step, AI can study existing systems and recommend:
- triggers
- actions
- routing rules
For example, if two systems frequently exchange certain types of data, AI can auto-suggest a workflow that developers can refine instead of building from scratch.
-
Predicting System Failures Before They Happen
Integrations break most often because of:
- API limits
- format changes
- server downtime
- unexpected traffic spikes
ML models track these patterns over time and alert the team before something collapses. You get early warnings like: “This API may slow down tomorrow” and “This workflow might fail due to unusual traffic”
As a result, teams respond proactively instead of firefighting.
-
Intelligent API Management
Modern systems depend heavily on APIs. AI improves API management by:
- spotting high-risk requests
- identifying unused or duplicate endpoints
- predicting capacity requirements
- helping optimize request flows
-
Faster Testing with AI
Testing integrations manually is slow because every connection has its own behavior.
AI speeds this up by:
- generating test cases automatically
- learning from previous integration failures
- validating edge cases
- simulating API responses
-
Real-Time Anomaly Detection
AI watches the flow of data and system behavior in real time. If something looks “off,” it flags it immediately. Examples include:
- sudden spikes in response time
- mismatched data formats
- repeated retries
- incomplete payloads
This helps teams catch hidden issues long before they turn into large-scale failures.
-
Improved Security DuringIntegration
Security risks often slip through integrations outdated keys, insecure endpoints, or misconfigured permissions. AI strengthens security by:
- spotting unusual access patterns
- flagging suspicious API calls
- identifying weak configurations
- checking compliance automatically
It acts like a 24/7 security analyst monitoring every interaction.
In the bigger picture, AI and ML are no longer “add-ons” in software integration. They’ve become core to how modern systems talk to each other.
Tools Used for Software Integration
| Tool / Platform | What It’s Used For |
| Zapier | Connects apps and automates small tasks without coding. |
| MuleSoft | Connects different systems and APIs across a company. |
| Boomi | Builds integrations quickly using drag-and-drop. |
| Power Automate | Automates tasks inside the Microsoft ecosystem. |
| Apache Camel | Helps developers connect apps using many protocols. |
| Postman | Tests and checks APIs to make sure integrations work. |
| Jitterbit | Connects data, apps, and APIs with visual tools. |
| Workato | Creates automated workflows between business apps. |
| Informatica Cloud | Moves and cleans data across different systems. |
| AWS Step Functions | Builds serverless workflows inside AWS. |
| Google Pub/Sub | Sends messages between services in real time. |
| IBM App Connect | Connects enterprise apps and data sources. |
| Talend | Integrates and transforms data across platforms. |
| N8N | Self-hosted workflow automation that keeps data in-house. |
Conclusion
In 2026, software integration isn’t just a technical upgrade, it’s the backbone that keeps modern businesses running smoothly. With companies relying on dozens of tools every day, disconnected systems quickly lead to slow decisions, scattered data, and unnecessary manual work.
But when your CRM, ERP, HR, finance, and support tools communicate seamlessly, everything becomes faster, clearer, and easier to manage.
The challenges mismatched data, scaling issues, and system conflicts are real, but they’re all fixable with strong integration practices, APIs, cloud connectors, and AI-driven automation. Simply put, integration is what ties your entire digital ecosystem together. Investing in it now makes your business sharper, more efficient, and ready for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does software integration mean?
A software integration represents joining two or rather more applications in such a way that they communicate and invoke operations and perform as a single system. Rather than the teams keeping various tools in sync manually, with integration, all of the tools will keep moving in real-time.
What are the uses of APIs in the integration of software?
APIs act like translators. They enable two applications to share information in real-time without any miscommunication. Whenever a customer makes a payment, their email addresses are notified, or an order of progress is shown, APIs will do the event tracking that makes it work.
What are the tools that are widely utilized in integration?
Mulesoft, Zapier, Boomi, Make, Workato, and custom API gateways are all popular. In the case of enterprises, iPaaS and cloud-native services of AWS, Azure, and GCP are widely adopted as secure and scalable integration.
What is the distinction between software and system integration?
Software integration refers to being able to connect two applications (such as CRM – Email tool), whereas system integration refers to two or more layers of infrastructure (hardware, networks, devices, servers, and apps). Software integration is more limited and faster; system integration is more extensive and complicated.
Why are systems usually failing at integration?
Most relying causes are quite common that are the inappropriateness of data format, the deterioration of APIs, differences in version, and using old software that does not comply with the new form of communication. Also caused by a lack of data governance is inconsistent with records across platforms.









